How can you tell if your crops are Mg deficient ?

What role does magnesium play in plants?
Magnesium is the core of the chlorophyll molecule, and approximately 6-25% of magnesium is bound to chlorophyll. Under light, high concentration of magnesium ions and suitable pH value can catalyze the activity of specific enzymes, increase the capture affinity and turnover rate of carbon dioxide, and greatly improve the photosynthetic efficiency.
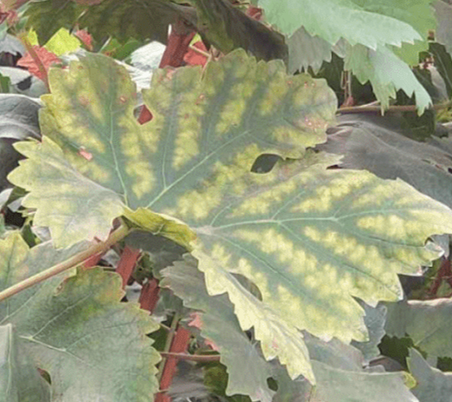

What are the symptoms of magnesium deficiency in plants?
The most typical symptom of magnesium deficiency in plants is chlorosis of leaves. The color of the leaf tips and leaf margins will fade, from green to yellowish, and it will spread to the base of the leaves. In severe cases, the leaves will dry up and fall off. In addition, there will be dwarf plants and slow growth.
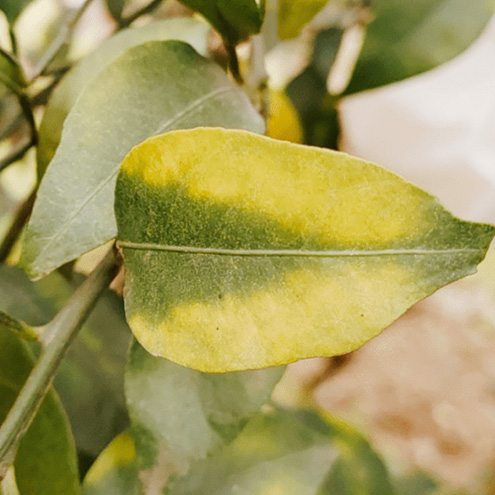

Do different crops require the same amount of magnesium?
Magnesium uptake averages between 10-25 kg per hectare per year for most crops, with broadleaf crops generally being around twice as much as cereals. Potatoes, sugar beets, fruit trees and greenhouse crops are most susceptible to magnesium deficiency.
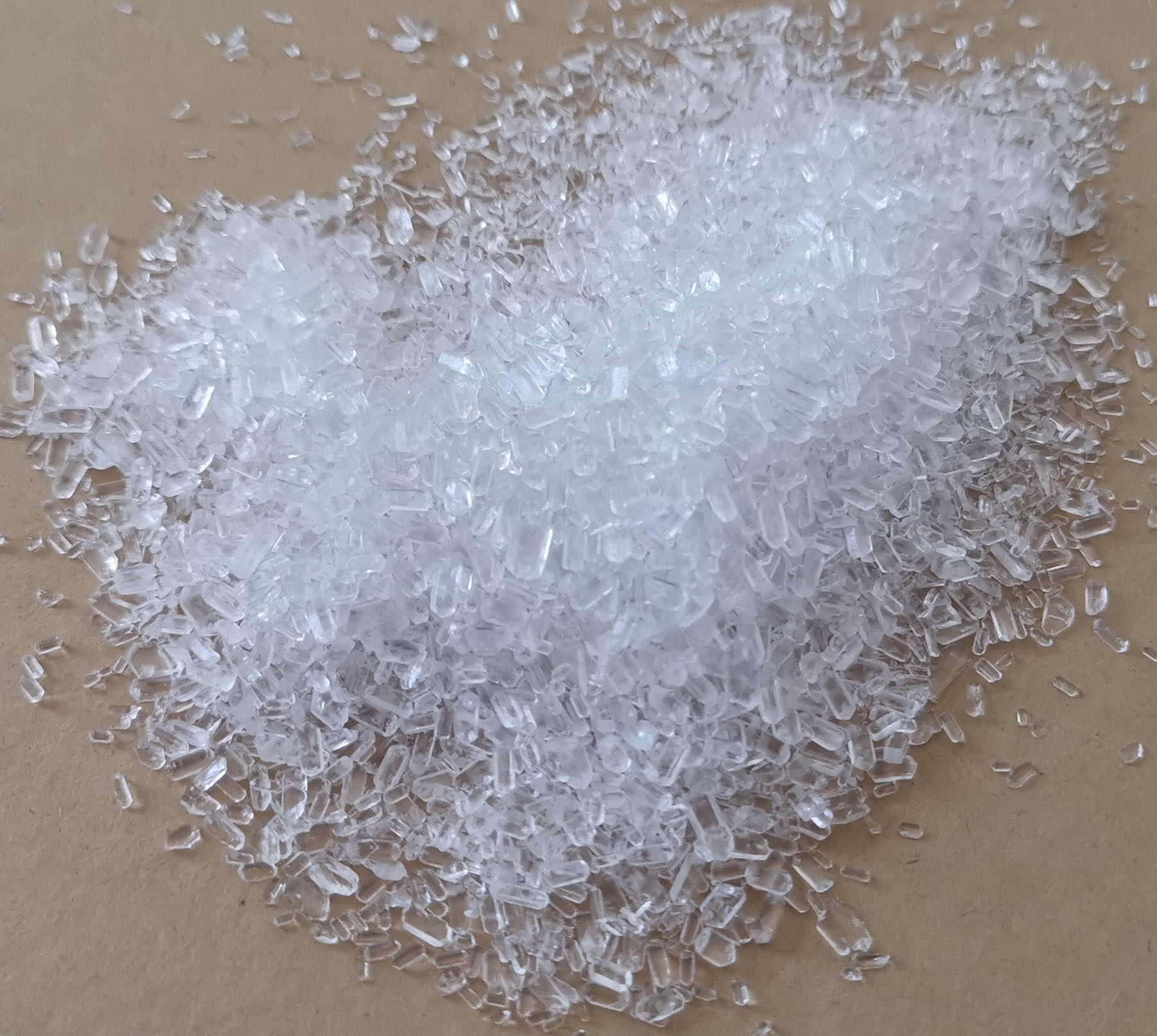

How do we supplement magnesium fertilizer?
When choosing the type of magnesium fertilizer, consideration should be given to the growth characteristics of crops, soil conditions and the convenience of field management. For long-term crops or as base fertilizers, alkaline incomplete water-soluble magnesium fertilizers can be selected, which have a certain effect on adjusting soil acidity; for short-term crops or as top-dressing fertilizers, fully water-soluble magnesium sulfate can be selected. Plots can be applied in combination with an irrigation system. Short-term relief of magnesium deficiency symptoms in plants, magnesium can also be quickly supplemented by foliar topdressing.
How can you tell if your crops are Mg deficient ?

What role does magnesium play in plants?
Magnesium is the core of the chlorophyll molecule, and approximately 6-25% of magnesium is bound to chlorophyll. Under light, high concentration of magnesium ions and suitable pH value can catalyze the activity of specific enzymes, increase the capture affinity and turnover rate of carbon dioxide, and greatly improve the photosynthetic efficiency.

What are the symptoms of magnesium deficiency in plants?
The most typical symptom of magnesium deficiency in plants is chlorosis of leaves. The color of the leaf tips and leaf margins will fade, from green to yellowish, and it will spread to the base of the leaves. In severe cases, the leaves will dry up and fall off. In addition, there will be dwarf plants and slow growth.

Do different crops require the same amount of magnesium?
Magnesium uptake averages between 10-25 kg per hectare per year for most crops, with broadleaf crops generally being around twice as much as cereals. Potatoes, sugar beets, fruit trees and greenhouse crops are most susceptible to magnesium deficiency.

How do we supplement magnesium fertilizer?
When choosing the type of magnesium fertilizer, consideration should be given to the growth characteristics of crops, soil conditions and the convenience of field management. For long-term crops or as base fertilizers, alkaline incomplete water-soluble magnesium fertilizers can be selected, which have a certain effect on adjusting soil acidity; for short-term crops or as top-dressing fertilizers, fully water-soluble magnesium sulfate can be selected. Plots can be applied in combination with an irrigation system. Short-term relief of magnesium deficiency symptoms in plants, magnesium can also be quickly supplemented by foliar topdressing.